About the bioregion
The Riverina bioregion lies in southwest New South Wales, extending into central-north Victoria. It goes from Ivanhoe in the Murray Darling Depression Bioregion south to Bendigo, and from Narrandera in the east to Balranald in the west.
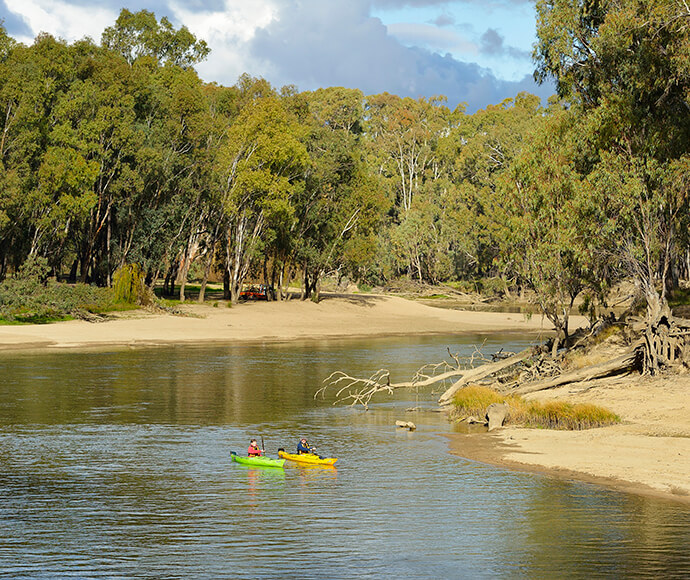
The Murray and Murrumbidgee Rivers and their major tributaries, the Lachlan and Goulburn Rivers, flow from the highlands in the east, westward across the Riverina plain.
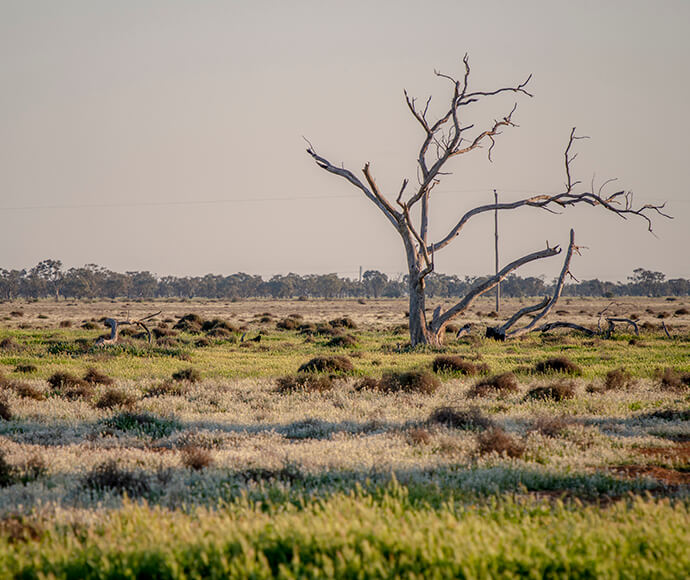
The climate is dry and semi-arid with hot summers and cool winters. Most rain falls in winter.
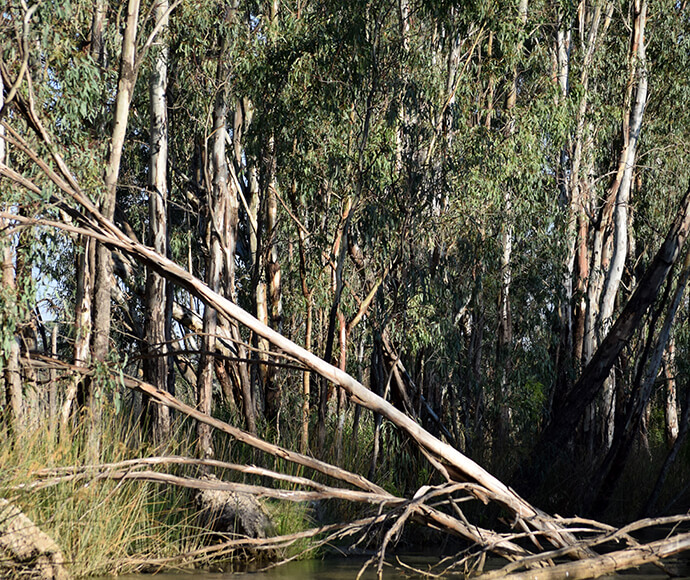
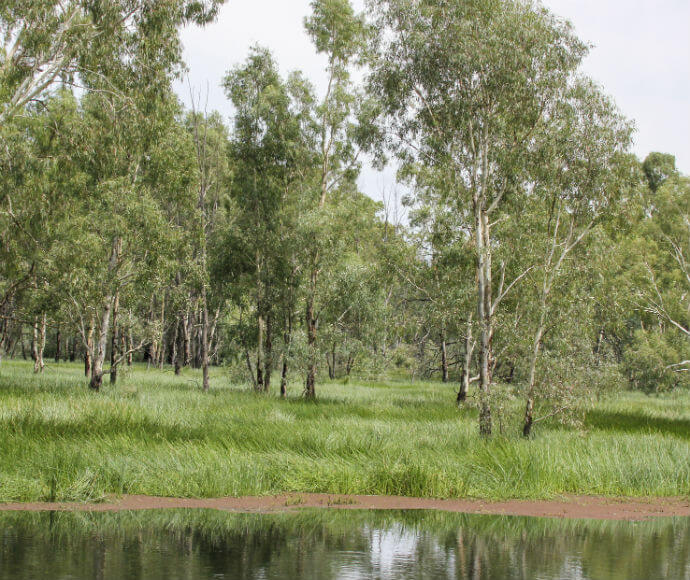
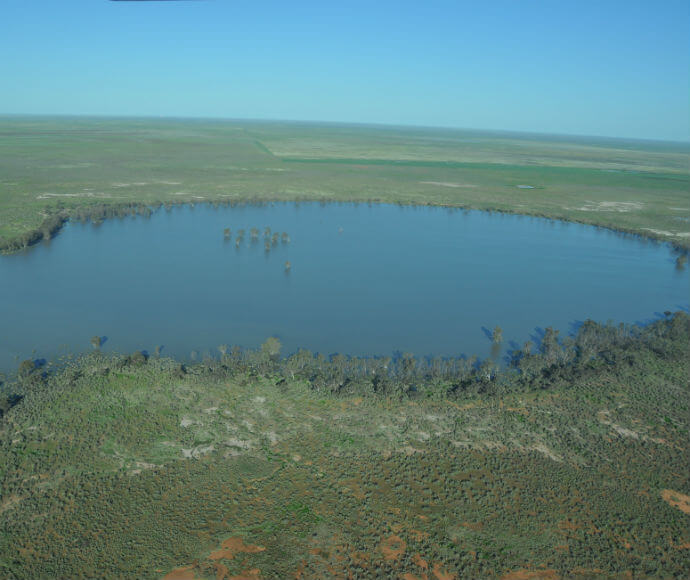
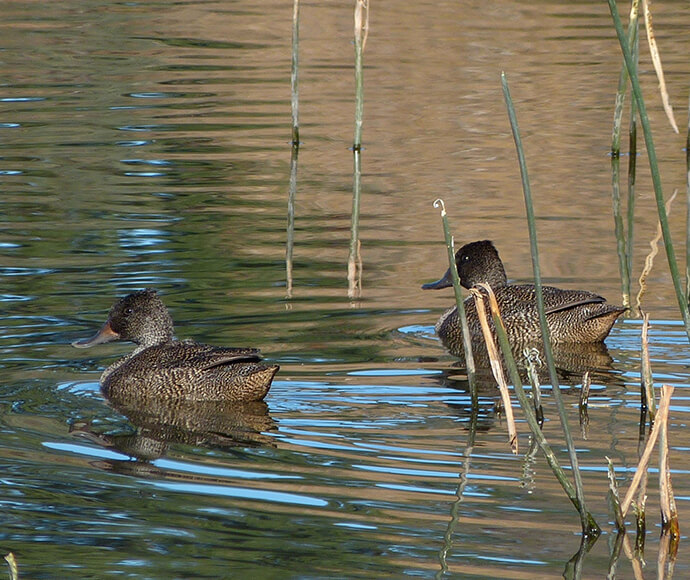
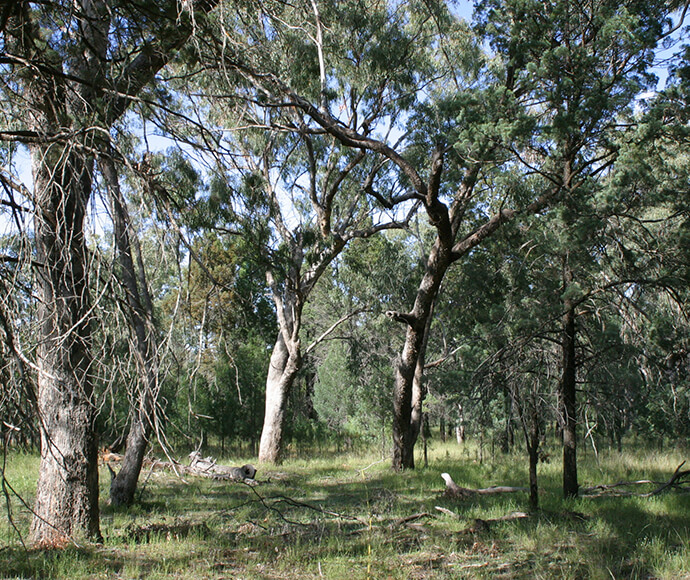
Vegetation ranges from river red gums, along river channels, to saltbush on the plains. There are several threatened species of both plant and animal in this bioregion. Several significant wetlands occur in the Riverina bioregion, including NSW Central Murray Forests and Fivebough and Tuckerbil Swamps, and these support many waterbirds, including migratory species.
The Riverina bioregion has several national parks and nature reserves.
Read Chapter 8, the Riverina Bioregion, in Bioregions of New South Wales: Their biodiversity, conservation and history for more information.
Bioregion area
- 9,704,469 hectares in total
- 7,030,950 hectares in New South Wales
Map showing the Riverina bioregion
Parks, reserves and conservation areas
This bioregion includes:






